A quiet revolution occurs in Africa, from remote villages to bustling city centers. Shops are morphing into mini-banks, offering essential financial services to millions who previously lacked Access.
This transformation is fueled by agency banking, a model where traditional banks partner with local businesses to extend their reach. These agents, typically grocery stores, post offices, or even individual entrepreneurs, become trusted hubs for basic banking needs like cash deposits, withdrawals, and bill payments.
Why is Agency Banking Booming in Africa?
Limited Access to traditional bank branches plagues many African countries. While mobile banking has grown, a significant portion of the population still prefers the convenience and personal touch offered by human interaction.
The Power of Numbers: Growth on an Upward Trajectory
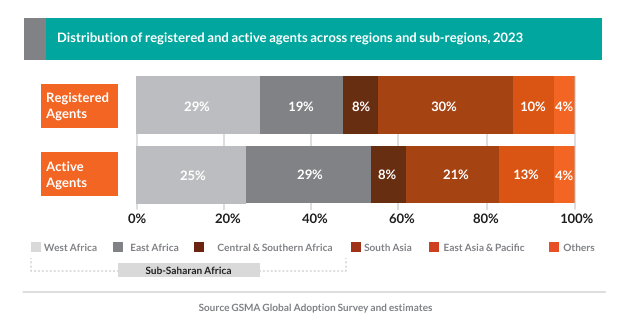
The success of agency banking is undeniable. According to a 2024 GSMA report, compared to 2022, registered agents grew by 22% in 2023 to reach 18.6 million, while active agents grew by 14% to 8.3 million. These agents were responsible for digitizing more than two-thirds of all the money entering the mobile money ecosystem: $307 billion in 2023, 12% higher than the previous year.
Agency banking bridges this gap, providing:
- Unmatched Accessibility: Banking services are brought directly to the people, eliminating long travel distances and saving time.
- Enhanced Convenience: Extended service hours and familiar settings cater to busy schedules and local preferences.
- Personalized Service: Agents act as trusted advisors, simplifying banking processes and fostering financial literacy.
The Benefits Go Beyond Convenience:
Banks and Financial Institutions:
- Expanding Access for the Unbanked and Underserved: Agency banking bridges the gap, reaching previously inaccessible populations.
- Building Long-Term Awareness: Increased brand visibility fosters customer loyalty and promotes financial services closer to home.
- Optimizing Cost Efficiency: Reduces operational costs compared to establishing new branches or ATM networks.
- Boosting Customer Acquisition and Retention: Studies have shown significant growth in customer onboarding and continued engagement through agency banking.
- Innovating for Strategic Differentiation: Allows banks to cater to the growing demand for convenience and personalize their offerings, enhancing their market presence.
Impact on Customers:
- Convenient Financial Services: These services eliminate the need for long journeys, offering extended hours and personalized service from local agents.
- Elevating Financial Literacy: Increased exposure to banking services facilitates learning through practical experience and interaction with agents.
- Local Economic Growth: This program provides Access to financial tools like loans, savings, and payments, stimulating local economies and empowering entrepreneurs.
The Success Story Unfolds:
Kenya serves as a prime example. Over 30,000 outlets are currently enrolled as bank agents. Some banks, like Co-operative, have partnered with cash-rich Savings and Credit Cooperative Societies to roll out their products effectively. However, owing to the short period within which the agency banking model has existed, the extent to which it can benefit banks, their clients, and the economy still needs to be studied. This necessitated the researchers conducting this study to analyze the role of agency banking in enhancing the financial sector’s deepening into unbanked emerging markets.
Transaction volumes handled by bank agents skyrocketed from $29.9 million in 2012 to $158 million in 2022. Institutions like Equity Bank, with a nationwide network of over 53,000 agents, have been at the forefront of this transformation.
Similarly, one Nigerian’s bank boasts a network exceeding 50,000 agents, contributing to the country’s impressive 600,000+ agent network. Enabling banks to optimize costs and accelerate agency banking growth across Africa.
Looking Ahead: A Brighter Financial Future
The Players Behind the Transformation
Five key players collaborate to make agency banking a success:
- Financial Service Providers (FSPs) or Banks: Banks leverage agency networks to reach underserved populations, expanding their customer base without the hefty costs of establishing new branches.
- Authorized Agents: Local businesses, empowered with training and technology, become the face of the bank in their communities.
- Customers: This model allows individuals lacking bank accounts or Access to traditional branches, promoting financial inclusion.
- Regulatory Authorities: Government oversight ensures compliance with financial regulations, protecting consumers and maintaining financial stability.
- Technology Providers: Their hardware and software solutions ensure secure and efficient transactions, facilitating the smooth operation of agency banking networks.
Agency banking empowers individuals and communities across Africa by bridging the physical gap and fostering financial literacy. There is interesting case study on Equity Bank using Agency Banking that served a customer base of over 9 million. Same we can expect an even broader reach and a more inclusive financial future for the continent as technology and partnerships are evolved.

