Mobile banking has revolutionized the financial services industry by allowing customers to access their bank accounts, perform transactions, and monitor their finances from their mobile devices. As the world becomes increasingly digitalized, customers are demanding 24/7 access to their accounts and seamless banking services. With the proliferation of smartphones, which have become a staple in everyday life, mobile banking has emerged as a convenient and secure alternative to traditional banking channels. In this blog, we will explore the concept of mobile banking, the different delivery channels associated with Mobile Banking, and the risks and benefits of mobile banking.
What is Mobile Banking?
Mobile banking allows customers to perform various banking transactions such as checking account balances, transferring funds, paying bills, and managing investments directly from their smartphones. Mobile banking provides customers with a high degree of convenience and flexibility, enabling them to carry out their banking needs at any time and any place they wish. Mobile banking has become extremely popular due to the high penetration rate of smartphones, with over half of the global population owning a smartphone. In addition, mobile banks are also able to provide cost savings to both the customers and the banks by reducing the need for physical branches and overhead costs.
Mobile Banking Invention
Mobile banking can be traced back to the early days of mobile phone technology. The concept of mobile banking was first discussed in the 1990s, and the first mobile transaction was reportedly conducted in 1997, when a customer in Helsinki, Finland, used his mobile phone to purchase a bus ticket.
The Bank of Scotland is unquestionably a global mobile banking pioneer. In 2007, it announced the world’s first mobile banking app for smartphones. The first bank to provide mobile banking facilities in India was ICICI Bank in 1999, followed by HDFC Bank and IDBI Bank.
Today, the banking industry is investing heavily in mobile banking technology, with many leading banks developing their own mobile apps and partnerships with mobile network operators to offer mobile banking services to their customers.
The Global Mobile Banking Market is valued at USD 772.96 Million in 2022 and is projected to reach a value of USD 1873.23 Million by 2030. The Global Market is projected to grow, exhibiting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.70% over the forecast period.
Mobile Banking Delivery Channels
Mobile Banking offers customers the convenience of performing banking transactions anytime and anywhere without the need to visit a physical branch. Mobile Banking can be accessed through various delivery channels such as Short Message Service (SMS), Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD), Web Access Protocol (WAP), SIM Tool KIT (STK), Progressive Web Apps (PWA), and Mobile Apps.
Mobile banking is just one of the many delivery channels available to customers looking to access their bank accounts and perform financial transactions on the go. In addition to mobile apps, several other delivery channels are available for mobile banking, each with pros and cons.
Short Message Service (SMS) Banking [Old Technology]
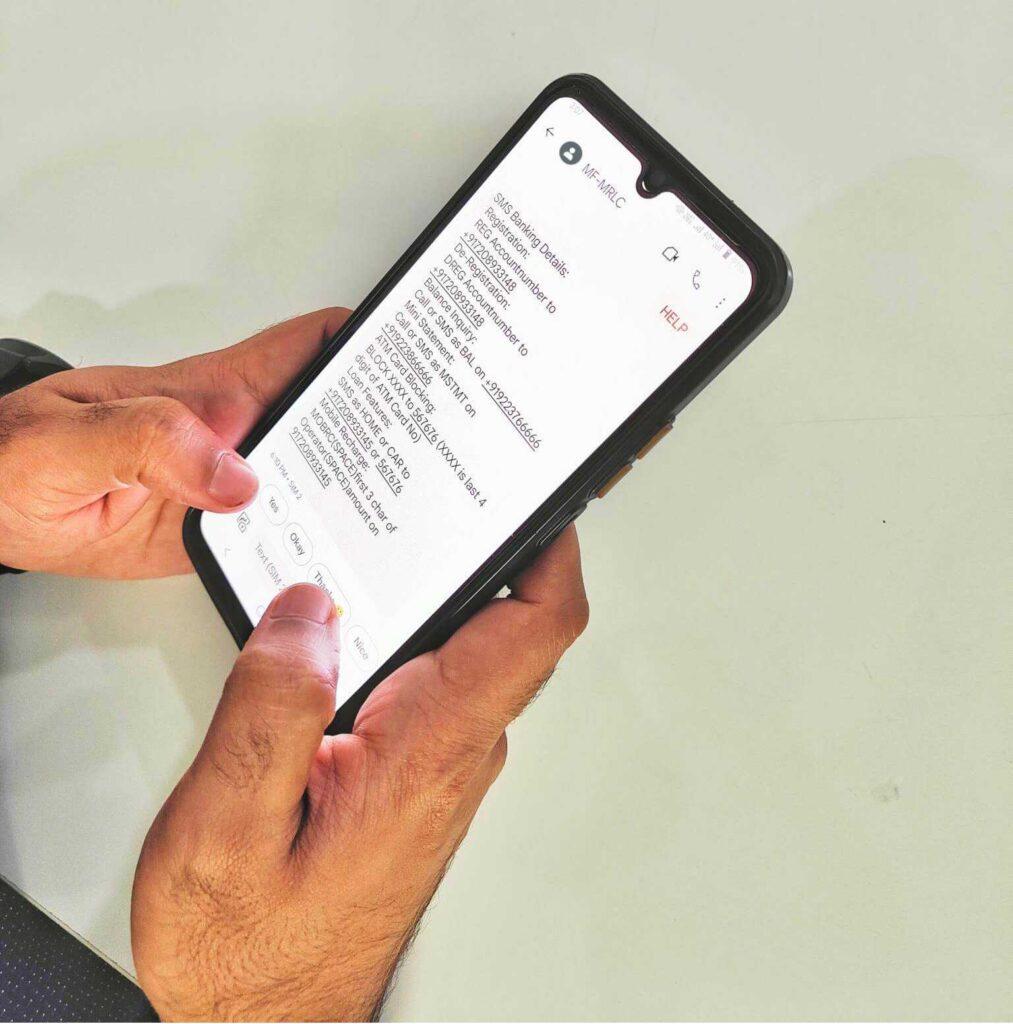

SMS banking, also known as mobile banking, is a financial service that allows customers to perform a variety of banking transactions via text message. This includes checking account balances, retrieving transaction histories, transferring funds, and paying bills. To use SMS banking, customers send a text message to a designated short-code or mobile number, followed by a set of commands instructing the bank’s system to perform the requested transaction.
One of the main advantages of SMS banking is convenience. Customers can perform banking transactions anywhere, anytime, without a mobile app or internet connection. This makes it an attractive option for customers who may not have access to a smartphone or computer, such as the elderly or those in remote areas with limited internet connectivity. SMS banking is also relatively inexpensive, as customers only pay to send a text message.
One of the main disadvantages of SMS banking is the limited set of transactions that can be performed. Customers are unable to access their accounts in real time, and they are limited to simple transactions such as checking account balances and transferring funds. Additionally, sending text messages can be slow, as customers must wait for the bank’s system to receive and process their commands.
Another disadvantage of SMS banking is security. Text messages can be intercepted or intercepted, exposing customers’ personal and financial information. This is particularly concerning when customers perform transactions, such as transferring funds, as scammers can easily manipulate the process. Banks and telcos that offer SMS banking services must ensure that their systems are secure and that customers are educated on the risks of SMS banking.
Another disadvantage is the need for customers to memorize complicated commands to perform transactions. This can be confusing for some customers, particularly those who are not familiar with technology or are not comfortable with text-based transactions.
USSD Banking [Old Technology, However, most popular is Africa]
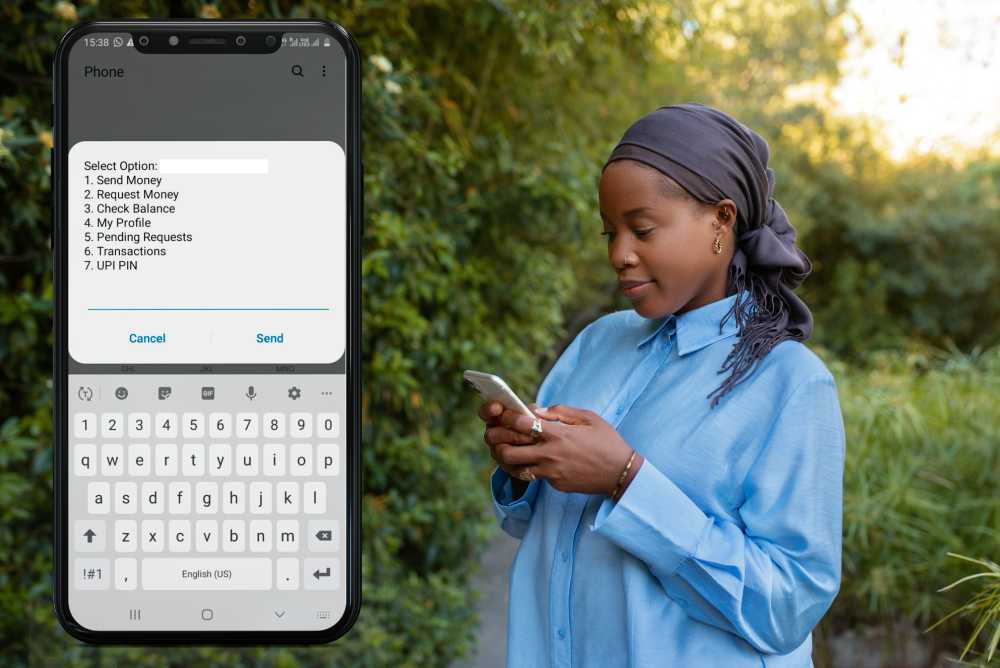
USSD, or Unstructured Supplementary Service Data, is a protocol that allows users to access information and perform transactions via their mobile phones by sending text messages to a dedicated short-code. USSD banking is a mobile banking service that enables customers to conduct basic banking transactions on their mobile phones using simple text messages. The service allows customers to check their account balance, transfer funds, and make bill payments from anywhere, anytime, without needing an app or internet connection.
One of the main advantages of USSD banking is that it allows customers to perform banking transactions from their mobile phones without needing an internet connection or a mobile banking app. This makes it an attractive option for customers who may not have access to a high-speed internet connection, such as those in rural areas or developing countries. USSD banking is also relatively inexpensive, as customers only pay the cost of sending a text message, which is usually a fraction of the cost of a phone call.
One of the main disadvantages of USSD banking is its limited functionality. Customers are limited to basic transactions, such as checking their account balance and transferring funds, and the service is not available for all banks. Another disadvantage is the security risks associated with the service. Since data is transmitted via text messages, there is a risk of interception or interception, exposing customers’ personal and financial information.
Banks and telcos that offer USSD banking services must ensure that their systems are secure and that customers are educated on the potential risks.
Sim Tool Kit (STK) Banking [Telco Dependent]
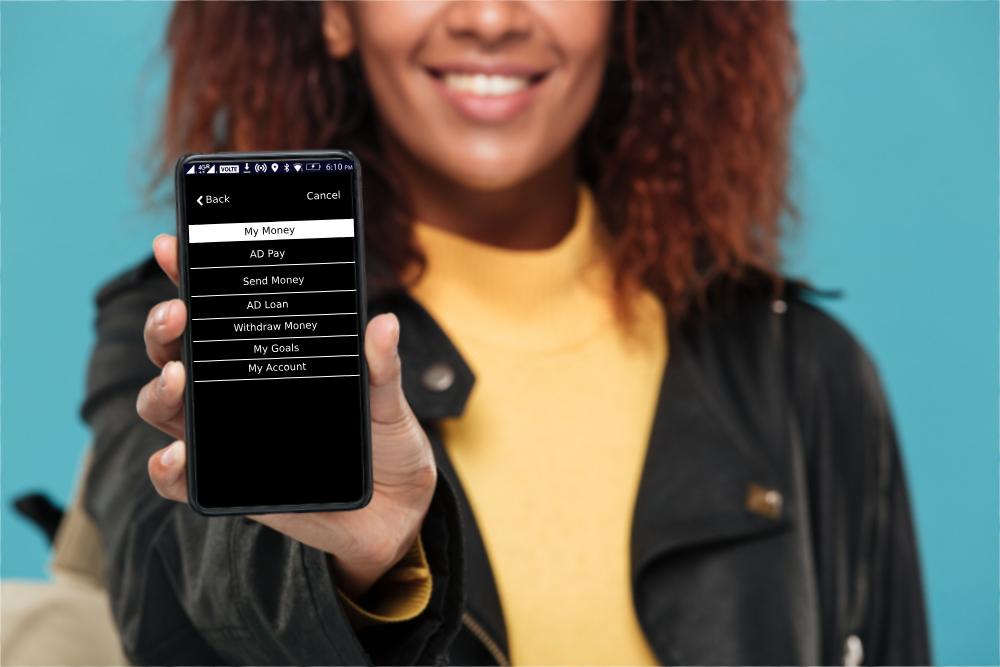
Sim Tool Kit, or STK, is a technology standard that allows mobile devices to perform a wide range of tasks related to mobile communication, such as making calls, sending text messages, accessing the internet, and accessing banking services. The GSM Association developed STK, which banks and telcos initially used to provide mobile banking services.
To use STK for mobile banking, the bank would burn the mobile banking app onto the SIM card of the customer’s mobile phone. This allowed customers to access their banking services directly from their mobile phones.
The main advantage of STK banking is convenience. It enables customers to access their banking services anywhere, anytime, without needing an internet connection or a separate device. Additionally, it can provide customers with real-time account updates, allowing them to track their account balance and activities.
However, there are some disadvantages to STK banking as well. One of the biggest is the potential for customers to damage or lose their SIM card. This can result in losing access to their bank account, and recovering a lost SIM card can be time-consuming and frustrating.
Another concern for the Service Provider is to Add or Remove the specific Service or change the Service flow.
WAP Banking & PWA Banking [Something like Internet Banking, However, has security concerns]
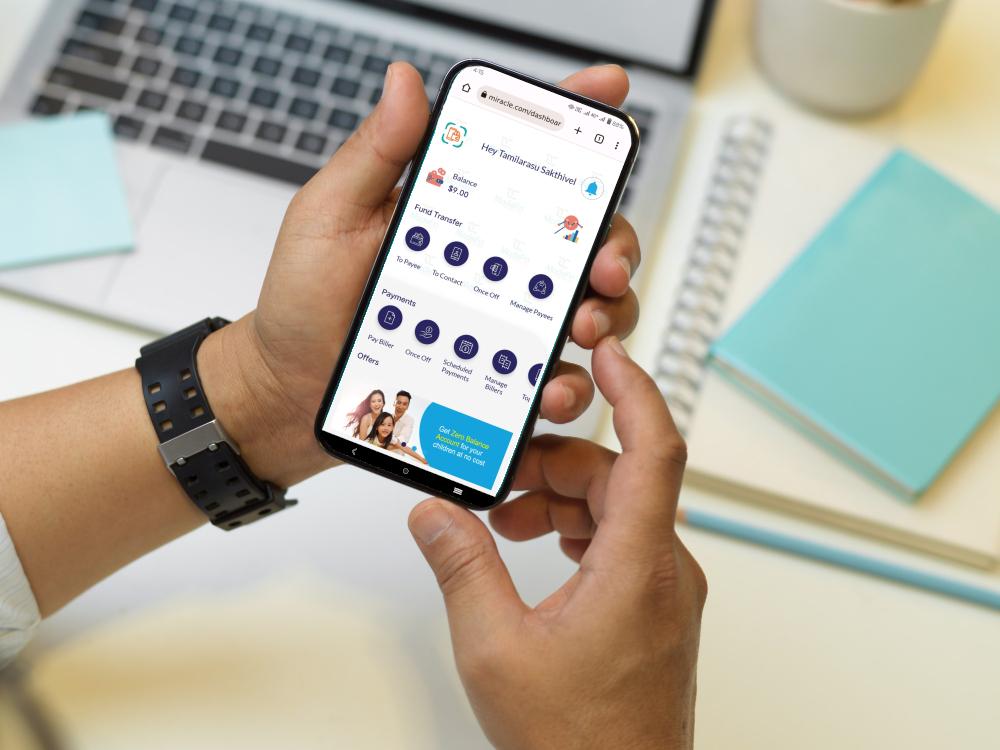
Web applications, or PWAs (Progressive Web Applications), and Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) banking are two types of mobile banking services that allow customers to access their bank accounts and perform banking transactions via their mobile devices.
WAP banking is a mobile banking service that uses WAP technology to allow customers to access their bank accounts and perform banking transactions via their mobile phones. WAP is a protocol that allows wireless devices, such as mobile phones, to access web-based applications. Banks typically offer WAP banking and require customers to visit a special WAP website to access their accounts.
One of the main advantages of WAP banking is that it allows customers to access their bank accounts and perform banking transactions from their mobile phones without the need to install a mobile banking app. This makes it an attractive option for customers who may not have access to high-speed internet connections. WAP banking is also relatively inexpensive, as customers only pay to access the WAP website.
One of the main disadvantages of WAP banking is that the technology is outdated and not widely used. WAP technology was developed in the early 2000s and has been largely replaced by more modern and efficient mobile technologies. WAP banking is also not suitable for more complex banking transactions.
PWA (Progressive Web Applications) banking is a newer mobile banking service allowing customers to access their bank accounts and perform banking transactions via mobile devices. PWAs are web-based applications that offer a more native-like experience, allowing customers to add them to their home screen and similarly access them to traditional apps. Banks typically provide PWA banking, available on iOS and Android devices.
One of the main advantages of PWA banking is that it offers a more seamless and user-friendly mobile banking experience. Customers can access their bank accounts and perform banking transactions from their mobile devices without needing a mobile banking app. PWAs are also more secure than traditional web applications, as they use modern web technology to encrypt data and protect customer information.
One of the main disadvantages of PWA banking is that the technology is relatively new and may not be widely supported by all banks.
Mobile Banking Apps [Most Popular and currently referred to as Mobile Banking]
Mobile banking apps are software applications that allow customers to access their bank accounts and perform banking transactions from their mobile devices. Mobile banking apps are available on various operating systems, including Android, iOS, and Huawei.
One of the main advantages of mobile banking apps is that they offer an all-in-one mobile banking solution, allowing customers to perform various banking transactions, including checking account balances, transferring funds, paying bills, and applying for loans, all from their mobile devices. Mobile banking apps also offer customers convenience and a rich user experience. Its benefits include enhanced security and a customizable interface. However, its limitations include dependency on the app store and the mobile phone manufacturer, which may restrict its availability to potential customers.
Another advantage of mobile banking apps is that they allow customers to manage their finances more efficiently. Mobile banking apps typically offer budgeting tools and expense-tracking features, allowing customers to track their spending and stay on top of their expenses.
Mobile app banking has become one of the most popular ways users can access banking services on their smartphones. However, like any online activity, there are risks associated with mobile app banking. Some risks related to mobile app banking include hacking, identity theft, information fraud, and security breaches.
Sometimes, mobile banking apps can be challenging for some customers, particularly those who are not tech-savvy or uncomfortable with technology. Mobile banking apps can also be complicated for customers with multiple bank accounts or needing more complex financial services.
Conclusion
A recent survey indicates an exceptionally high adoption rate among digital banking users, with 89% of customers using their mobile devices for banking operations. Among millennials, this number rises even further to 97%.
In conclusion, Mobile Banking has revolutionized how customers access financial services and has become an essential part of everyday life. Mobile Banking technology has evolved significantly over the last few years. The market penetration of mobile banking is growing rapidly, with consumers having access to a wide range of mobile banking delivery channels, including SMS, USSD, WAP, PWA, and Mobile Apps.
Mobile App Banking has become an essential part of the banking sector. Banks must choose a reliable and innovative Technology service provider, such as Modefin , to stay safe and secure while providing mobile banking services. Modefin provides an innovative Mobile Banking solution that offers multiple delivery channels, including SMS, USSD, WAP, STK, PWA, and Mobile Apps.
Today, almost all Banks offer Mobile Banking, and if you are still thinking before it’s too late, implement it.
If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to comment, or if you want me to cover any specific topic, do write to me.

